A variety of topics were presented in the 1996 Case Study columns. The following 44 questions will
A variety of topics were presented in the 1996 Case Study columns. The following 44 questions will allow you to review the 11 columns and determine your diagnostic skills. After completing the Case Study test, turn to page 31 to check your answers.
Joen Iannucci Haring, DDS, MS
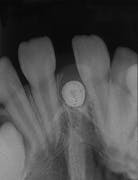
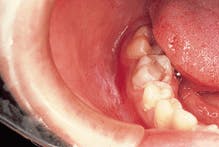
Case 1
Mesiodens
1. Identify the most common location for the mesiodens.
a. midline of mandible
b. midline of maxilla
c. angle of mandible
d. posterior maxilla
e. none of the above
2. Identify the radiographic appearance of the mesiodens.
a. tooth-like radiolucency
b. tooth-like radiopacity
c. ground glass radiopacity
d. multilocular radiolucency
e. none of the above
3. Identify the best method to diagnose a mesiodens.
a. clinical appearance
b. histologic appearance
c. cytologic appearance
d. radiographic appearance
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning the mesiodens.
a. often remains impacted
b. often symptomatic
c. often fast-growing
d. often occurs in multiples
e. often occurs with tumors
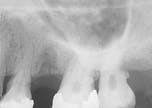
Case 2
Condensing Osteitis
1. Identify the most common location for condensing osteitis.
a. mandibular incisor area
b. mandibular ramus area
c. mandibular molar area
d. maxillary premolar area
e. maxillary incisor area
2. Identify the radiographic appearance of condensing osteitis.
a. solitary radiopacity
b. multilocular radiolucency
c. cotton wool radiopacity
d. ground glass radiopacity
e. irregular radiopacity
3. Identify the treatment of choice for condensing osteitis.
a. radiation therapy
b. antibiotic therapy
c. surgical excision
d. extraction or RCT
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning condensing osteitis.
a. often symptomatic
b. often involves a vital tooth
c. often occurs in children
d. often appears as a mini-tooth
e. often involves teeth #19 and #30
Case 3
Drug-related gingival hyperplasia
1. Identify the drug that is not a cause of drug-related gingival hyperplasia.
a. dilantin
b. nifedipine
c. phenytoin
d. cyclosporin
e. phenergan
2. Identify the major predisposing factor for drug-related gingival hyperplasia.
a. heavy smoking
b. increased stress
c. poor oral hygiene
d. patient age and sex
e. none of the above
3. Identify the best method to diagnose drug-related gingival hyperplasia.
a. history and appearance
b. histologic examination
c. cytologic examination
d. radiographic examination
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning drug-related gingival hyperplasia.
a. gingival tissues always appear in-flamed
b. histologic appearance is non-diagnostic
c. no effective treatment is available
d. disappears spontaneously
e. none of the above
Case 4
Periodontal Abscess
1. Identify the treatment of choice for a periodontal abscess.
a. surgical excision
b. drainage of periodontal pocket
c. antifungal therapy
d. improved oral hygiene
e. antimicrobial rinses
2. Identify the typical appearance of the periodontal abscess.
a. ulcerative mass
b. erythematous mass
c. white plaque
d. fissured area
e. none of the above
3. Identify the symptoms associated with the periodontal abscess.
a. slow onset, mild pain
b. slow onset, severe pain
c. sudden onset, mild pain
d. sudden onset, severe pain
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning the periodontal abscess.
a. foreign bodies often initiate this lesion
b. always associated with a non-vital tooth
c. bone destruction occurs very slowly
d. pus drainage is uncommon
e. diagnosis is based on a biopsy
Case 5
Eruption Cyst
1. Identify the origin of the eruption cyst.
a. viral
b. bacterial
c. autoimmune
d. developmental
e. none of the above
2. Identify the age group associated with the eruption cyst.
a. children
b. young adults
c. adults
d. elderly
e. any of the above
3. Identify the treatment of choice for the eruption cyst.
a. surgical excision
b. cryosurgery
c. antibiotic therapy
d. corticosteroid therapy
e. no treatment necessary
4. Identify the true statement concerning the eruption cyst.
a. painful when compressed
b. often appears ulcerated
c. appears pink or yellow
d. diagnosis is based on appearance
e. feels firm and well-defined
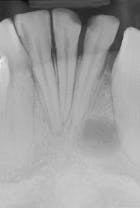
Case 6
Enamel Pearl
1. Identify the origin of the enamel pearl.
a. inflammatory
b. autoimmune
c. developmental
d. neoplastic
e. none of the above
2. Identify the population most often associated with the enamel pearl.
a. Asian
b. Caucasian
c. Hispanic
d. Mediterranean
e. none of the above
3. Identify the location of the enamel pearl.
a. any root surface
b. root surface near furcation
c. root surface near CEJ
d. any of the above
e. none of the above
4. Identify the best method to diagnose an enamel pearl.
a. patient history
b. histologic appearance
c. cytologic appearance
d. radiographic appearance
e. none of the above
Case 7
Residual Cyst
1. Identify the cyst that is identical to the residual cyst.
a. dentigerous cyst
b. radicular cyst
c. eruption cyst
d. lateral periodontal cyst
e. none of the above
2. Identify the radiographic appearance of the residual cyst.
a. unilocular radiolucency
b. multilocular radiolucency
c. mixed radiolucent-radiopaque
d. focal radiopacity
e. none of the above
3. Identify the best method to diagnose a residual cyst.
a. clinical appearance
b. histologic appearance
c. cytologic appearance
d. radiographic appearance
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning the residual cyst.
a. recurrence is unlikely
b. often symptomatic
c. disappears spontaneously
d. histologic appearance is non-diagnostic
e. no effective treatment is available
Case 8
Chemical Injury
1. Identify the agent(s) most likely to cause a chemical injury of oral tissues.
a. aspirin
b. hydrogen peroxide
c. silver nitrate
d. phenol
e. any of the above
2. Identify the true statement concerning a chemical injury of oral tissues.
a. tissue damage depends on contact time
b. tissue damage depends on agent concentration
c. coagulation necrosis occurs with increased exposure
d. amount of tissue damage correlates with amount of pain
e. any of the above
3. Identify the treatment of choice for a chemical injury of oral tissues.
a. antifungal medication
b. antibiotic medication
c. corticosteroid medication
d. palliative medication
e. none of the above
4. Identify the best method to diagnose a chemical injury of oral tissues.
a. history and appearance
b. histologic appearance
c. cytologic appearance
d. radiographic appearance
e. none of the above
Case 9
Tonsilloliths
1. Identify the location of a tonsillolith.
a. tonsillar crypt
b. floor of the mouth
c. mandibular ramus
d. salivary gland
e. none of the above
2. Identify the radiographic appearance of a tonsillolith.
a. unilocular radiolucency
b. multilocular radiolucency
c. radiopacity within bone
d. radiopacity within soft tissue
e. none of the above
3. Identify the best method to diagnose a tonsillolith.
a. patient history
b. clinical and radiographic appearance
c. histologic appearance
d. cytologic appearance
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning a tonsillolith.
a. easily identified on a periapical film
b. often results in bony expansion and pain
c. associated with a recurrent sore throat
d. always visible upon oral examination
e. none of the above
Case 10
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
1. Identify the most common location for the central giant cell granuloma.
a. anterior mandible
b. posterior mandible
c. anterior maxilla
d. posterior maxilla
e. posterior maxilla or mandible
2. Identify the most likely radiographic appearance of the central giant cell granuloma.
a. multilocular radiolucency
b. unilocular radiolucency
c. radiopacity with radiolucent rim
d. radiolucency with radiopaque flecks
e. none of the above
3. Identify the treatment of choice for the central giant cell granuloma.
a. none
b. cryosurgery
c. surgical excision
d. electrosurgery
e. radiation therapy
4. Identify the true statement concerning the central giant cell granuloma.
a. often occurs in persons under 30
b. males affected more often than fe-males
c. characterized by its soft tissue location
d. diagnosis based on radiographic appearance
e. often symptomatic
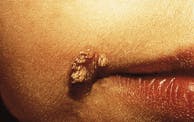
Case 11
Verruca Vulgaris
1. Identify the origin of verruca vulgaris.
a. viral
b. bacterial
c. fungal
d. parasitic
e. autoimmune
2. Identify the most common locations for verruca vulgaris.
a. lip, tongue, labial mucosa
b. lip, hard palate, floor of mouth
c. soft palate, hard palate, tongue
d. buccal mucosa, tongue, floor of mouth
e. none of the above
3. Identify the symptoms associated with verruca vulgaris.
a. burning
b. pain
c. bad taste
d. pruritus
e. none of the above
4. Identify the true statement concerning verruca vulgaris.
a. usually occurs in adults
b. often grows to a large size (> 1 cm)
c. affects skin and oral cavity
d. appears as a dome-shaped mass
e. is not contagious
See below for answers
Joen Iannucci Haring, DDS, MS, is an associate professor of clinical dentistry, Section of Primary Care, The Ohio State University College of Dentistry.
Case Study Test Answers
CASE 1: 1 = b; 2 = b; 3 = d; 4 = a
CASE 2: 1 = c; 2 = a; 3 = d; 4 = e
CASE 3: 1 = e; 2 = c; 3 = a; 4 = b
CASE 4: 1 = b; 2 = b; 3 = d; 4 = a
CASE 5: 1 = d; 2 = a; 3 = e; 4 = d
CASE 6: 1 = c; 2 = a; 3 = b; 4 = d
CASE 7: 1 = b; 2 = a; 3 = b; 4 = a
CASE 8: 1 = e; 2 = e; 3 = d; 4 = a
CASE 9: 1 = a; 2 = d; 3 = b; 4 = c
CASE 10: 1 = a; 2 = a; 3 = c; 4 = a
CASE 11: 1 = a; 2 = a; 3 = e; 4 = c